1. A2DP介绍
A2DP全名是Advanced Audio Distribution Profile 蓝牙音频传输协议 ,A2DP定义了ACL(Asynchronous Connectionless 异步无连接)信道上传送单声道或立体声等高质量音频信息的协议和过程 。 目前 A2DP 的最新版本为 1.3, 相关文档可以到 bluetooth.org 查看。
1.1 简介
- Source (SRC) : 用于输出音频流
- Sink (SNK) : 用于接收音频流
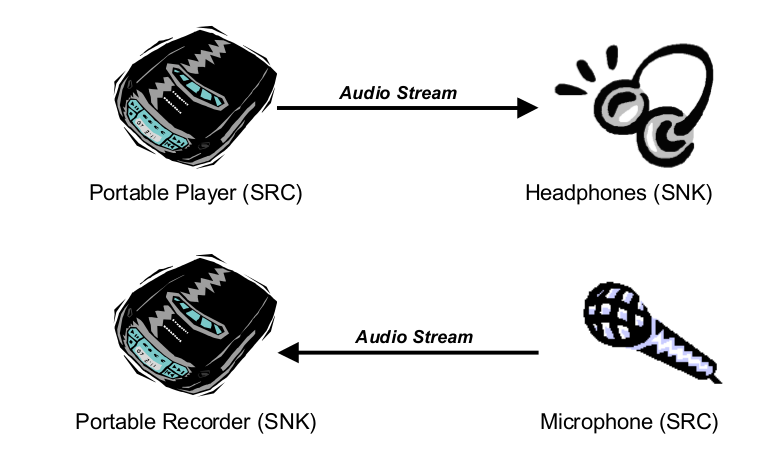
目前手机上基本都实现了 SRC role , 另外在部分的手机代码中也有看到实现 SNK 但 default 并没有enable .
A2DP协议基于 AVDTP (audio/video distribution transport protocol ), AVDTP则定义了蓝牙设备之间数据流句柄的参数协商,建立和传输过程以及相互交换的信令实体形式,该协议是A2DP框架的基础协议。
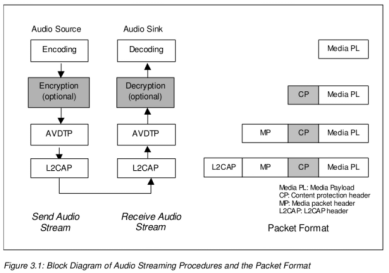
1.2 一些限制
(1) 不支持同步的一对多传输
(2) 在 Source 和 Sink 端的传输过程中要经过无线信号的传播, 数据buffer的传递 和 音频数据的编解码, 这样在SRC 和SNK 之间必然存在一定的延迟
(3) 音频数据的传输速率必须小于蓝牙链接的速率, 另外还需留出余地给重传
(4) A2DP 并不提供任何数据保护机制
1.3 编码
A2DP 规定 SRC 和 SNC 必须支持 SBC 编码, 另外还有很多其他的编解码类型 (例如当前很多设备支持的 aptx) 由 vendor 来决定添加。
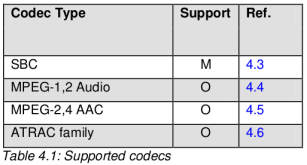
1.4 SBC编码
在 AVDTP signaling 过程中, 会获取codec 的information ,其中SBC information 的相关格式数据结构为 :
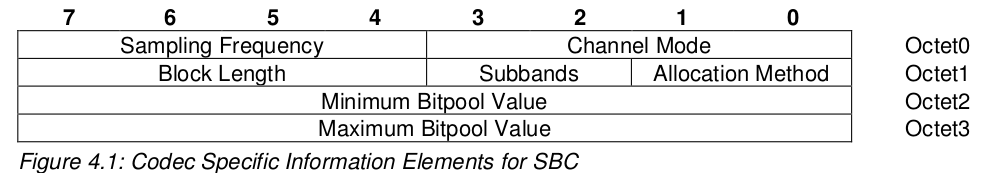
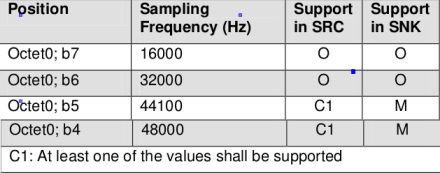
Sampling Frequency
SNK 必须至少支持 44100 和 48000 , 而 SRC 必须至少支持两者之一
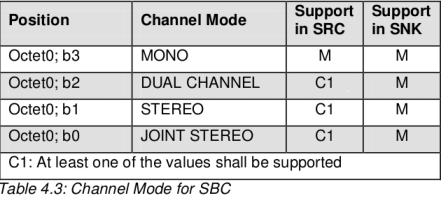
Channel Mode
其他参数这里不再列出, 具体可以查询 A2DP Spec
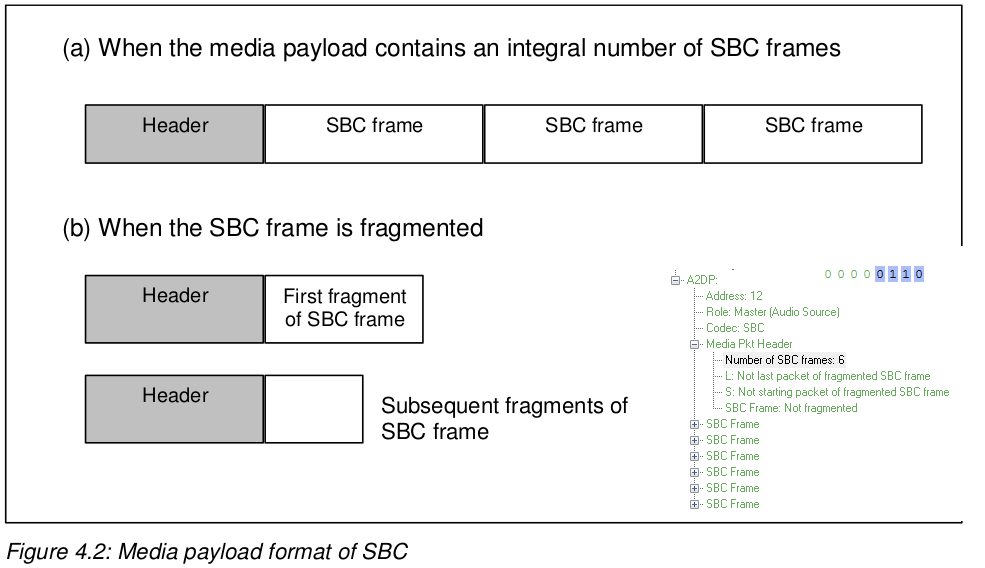
SBC 传输的帧结构如下 , 右下角为 snoop log 截图
1.5 通信过程
A2DP 基于AVDTP 连接之上, 先来看一下 AVDTP 中的两个重要概念
Stream End Point (SEP) : 提供具体传输特定 AV capabilities 功能的服务 , A2DP 中会根据不同的 codec 或者参数注册不同的 SEP
Stream End Point Identifier (SEID):标识Stream End Point的 ID
AVDTP 中主要会建立两种 channel 连接: Signalling Channel 和 Media Transport Channel
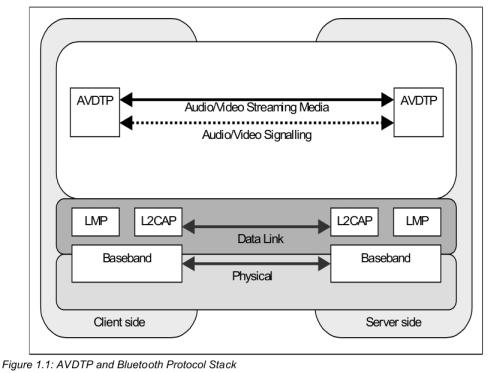
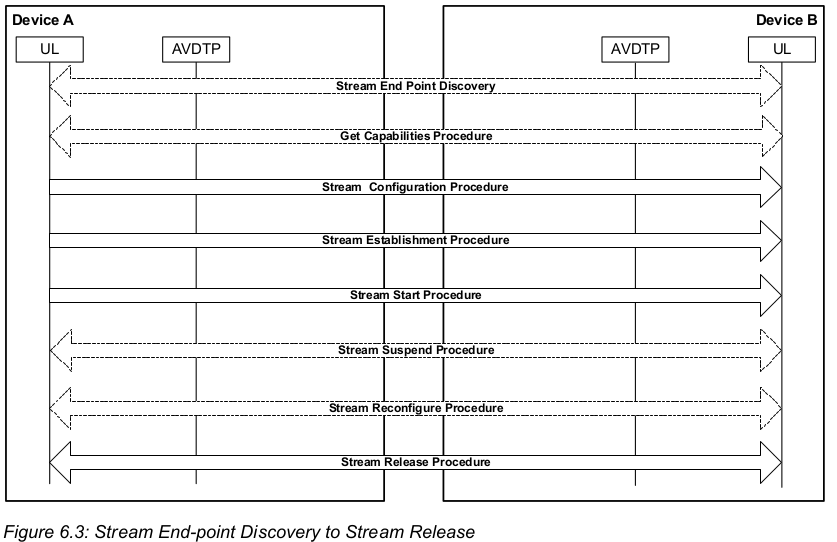
AVDTP 完整的 Stream End-point Discovery to Stream Release过程:
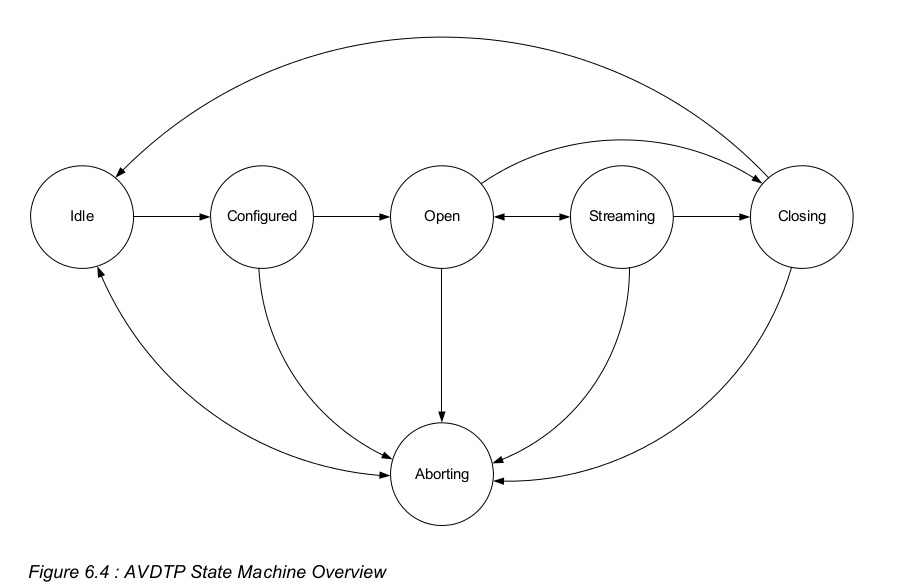
其中会有5个状态的切换 :
其主要流程有 :
Stream End Point Discovery :远端设备提供支持的SEP列表和media Type。
Get All Capabilities :通过SEID 获取SEP 的所有Capabilities
Stream Configuration :配置某个 SEP 的具体参数
Stream Establishment :opening of a transport session
Stream Start :在 transport session open 之后 , the Start Streaming procedure causes the streaming to start ; i.e., Media (Reporting, Recovery) packets can be exchanged
Stream Suspend : 代表 stream suspend
Stream Reconfigure:再次配置
Stream Release : Stream release is initiated by the upper layer within a device; a signal is sent indicating that a stream end-point be closed.
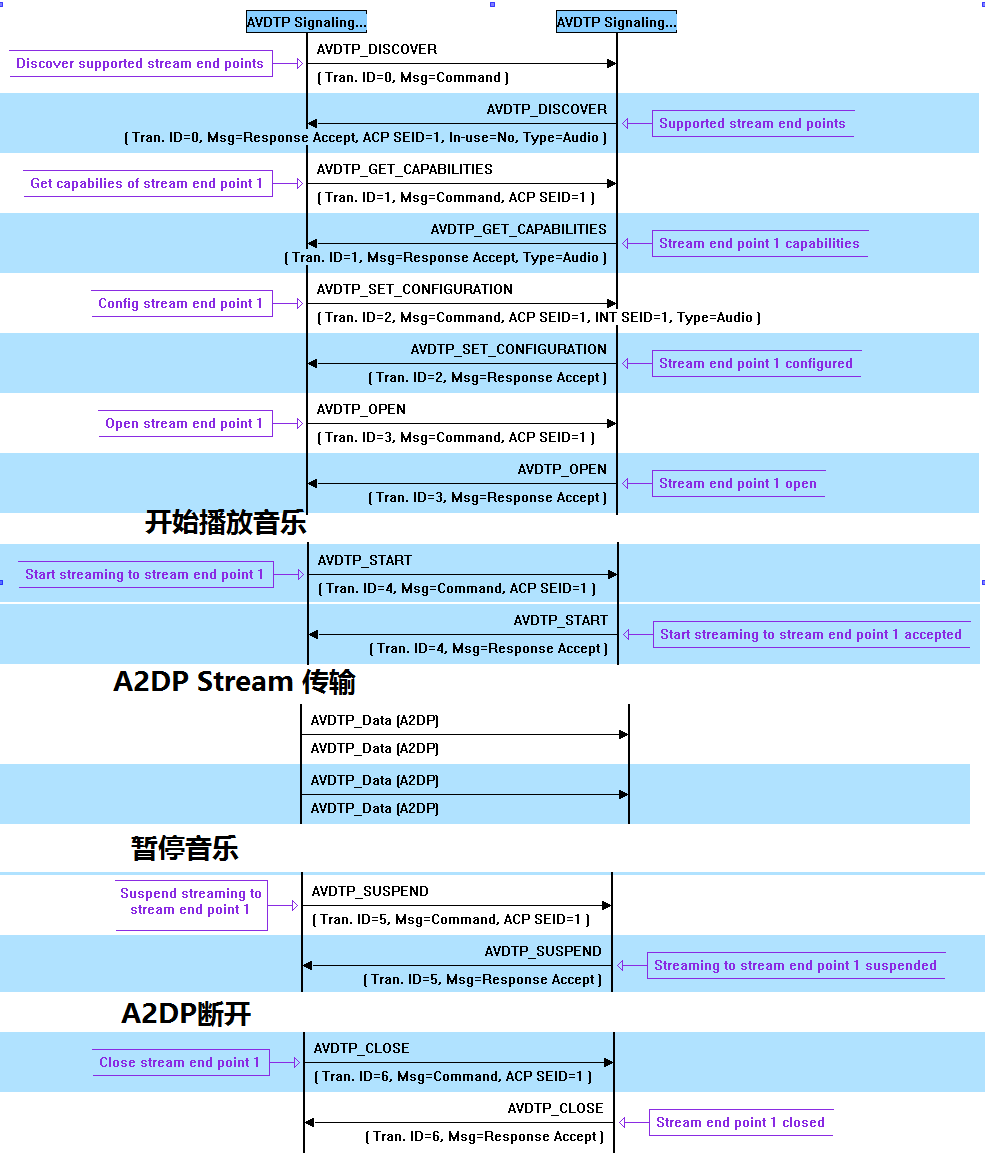
BT snoop log 实例 :
2. Android A2DP
2.1 API
先来看一下 A2DP 相关的 API , 代码路径在 frameworks/base/core/java/android/bluetooth/BluetoothA2dp.java
public方法如下, 只能获取一些状态信息 :
List<BluetoothDevice> getConnectedDevices();
int getConnectionState(BluetoothDevice device);
List<BluetoothDevice> getDevicesMatchingConnectionStates(int[] states);
boolean isA2dpPlaying(BluetoothDevice device);
hide方法如下, 可以操作连接断开及其他特性的设定 :
boolean connect(BluetoothDevice device)
boolean disconnect(BluetoothDevice device)
boolean setPriority(BluetoothDevice device, int priority)
int getPriority(BluetoothDevice device)
boolean isAvrcpAbsoluteVolumeSupported()
void adjustAvrcpAbsoluteVolume(int direction)
void setAvrcpAbsoluteVolume(int volume)
boolean shouldSendVolumeKeys(BluetoothDevice device)
static String stateToString(int state)
Broadcast & State
public static final String ACTION_CONNECTION_STATE_CHANGED =
"android.bluetooth.a2dp.profile.action.CONNECTION_STATE_CHANGED";
public static final String ACTION_PLAYING_STATE_CHANGED =
"android.bluetooth.a2dp.profile.action.PLAYING_STATE_CHANGED";
public static final int STATE_PLAYING = 10;
public static final int STATE_NOT_PLAYING = 11;
注意: 这里BluetoothA2dp 的构造函数并不是 public 不对外开放, 一般获取 BluetoothA2dp 的方法为通过 getProfileProxy 注册 listener , 当 BluetoothA2dp 与 A2dpService bind 成功之后回调注册的 listener 中的 onServiceConnected ,BluetoothA2dp 也会作为参数传过来 . 如下为代码示例 :
public A2dpDeviceStatus(Context mContext) {
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
mAdapter.getProfileProxy(mContext, mProfileListener,
BluetoothProfile.A2DP);
}
private BluetoothProfile.ServiceListener mProfileListener =
new BluetoothProfile.ServiceListener() {
public void onServiceConnected(int profile, BluetoothProfile proxy) {
if (profile == BluetoothProfile.A2DP) {
mA2dp = (BluetoothA2dp) proxy;
}
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(int profile) {
if (profile == BluetoothProfile.A2DP) {
mA2dp = null;
}
}
};
2.2 A2DP Service
以上API 实际是通过 Binder 调用 BT Service 中的 A2dpService 来执行
@ packages/apps/Bluetooth/AndroidManifest.xml
<service
android:process="@string/process"
android:name = ".a2dp.A2dpService"
<!-- 是否支持实例化, 一般默认为 true -->
android:enabled="@bool/profile_supported_a2dp">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.bluetooth.IBluetoothA2dp" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
2.2.1 Service Start
在蓝牙开启过程中会 enable 所有 supported Profile Services
void startCoreServices()
{
Class[] supportedProfileServices = Config.getSupportedProfiles();
//Startup all profile services
setProfileServiceState(supportedProfileServices,BluetoothAdapter.STATE_ON);
}
private void setProfileServiceState(Class[] services, int state) {
for (int i=0; i <services.length;i++) {
Intent intent = new Intent(this,services[i]);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ACTION,ACTION_SERVICE_STATE_CHANGED);
intent.putExtra(BluetoothAdapter.EXTRA_STATE,state);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
startService(intent);
}
}
其中 supportedProfileServices 最终是从 packages/apps/bluetooth/res/values/config.xml 中获取
<bool name="profile_supported_a2dp">true</bool>
<bool name="profile_supported_a2dp_sink">false</bool>
<bool name="profile_supported_hdp">true</bool>
<bool name="profile_supported_hs_hfp">true</bool>
<bool name="profile_supported_hfpclient">false</bool>
<bool name="profile_supported_hid">true</bool>
A2dpService 继承自 ProfileService , 其父类 onStartCommand 会调用到子类覆盖的 start 方法
@ packages/apps/Bluetooth/src/com/android/bluetooth/a2dp/A2dpService.java
protected boolean start() {
// 手机上一般仅支持连接1个a2dp设备, 不支持multiCast
mStateMachine = A2dpStateMachine.make(this, this,
maxConnections, multiCastState, offload_cap);
setA2dpService(this);
mAudioManager = (AudioManager) getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);
mAvrcp = Avrcp.make(this, this, maxConnections);
return true;
}
这里主要做了三件事 :
- 创建并启动 A2dpStateMachine ;
- A2dpService 实现单例模式, 其他service 通过 getA2dpService 获取到 A2dpService 对象
- 获取 AudioManager 代理对象
- 创建 Avrcp 对象
A2dpService 的功能实现主要是在 A2dpStateMachine ,A2dpStateMachine 状态机比较简单只有4个状态 :
 其中还会根据 bluedroid 中回调的 AudioState 记录设备的播放状态 。
其中还会根据 bluedroid 中回调的 AudioState 记录设备的播放状态 。
2.2.2 Service Init
@ packages/apps/Bluetooth/src/com/android/bluetooth/a2dp/A2dpStateMachine.java
static {
classInitNative();
}
private A2dpStateMachine(A2dpService svc, Context context, int
maxConnections, int multiCastState, String offload_cap) {
......
initNative(maxA2dpConnections, multiCastState, offload_cap);
}
找到这两个 Native 方法的映射 :
@ packages/apps/Bluetooth/jni/com_android_bluetooth_a2dp.cpp
static JNINativeMethod sMethods[] = {
{"classInitNative", "()V", (void *) classInitNative},
{"initNative", "(IILjava/lang/String;)V", (void *) initNative},
{"cleanupNative", "()V", (void *) cleanupNative},
{"connectA2dpNative", "([B)Z", (void *) connectA2dpNative},
{"disconnectA2dpNative", "([B)Z", (void *) disconnectA2dpNative},
{"allowConnectionNative", "(I[B)V", (void *) allowConnectionNative},
};
int register_com_android_bluetooth_a2dp(JNIEnv* env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, "com/android/bluetooth/a2dp/A2dpStateMachine",
sMethods, NELEM(sMethods));
}
static void classInitNative(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz) {
method_onConnectionStateChanged =
env->GetMethodID(clazz, "onConnectionStateChanged", "(I[B)V");
method_onAudioStateChanged =
env->GetMethodID(clazz, "onAudioStateChanged", "(I[B)V");
......
}
static void initNative(JNIEnv *env, jobject object, jint maxA2dpConnections,
jint multiCastState, jstring offload_cap) {
const bt_interface_t* btInf;
......
if ( (btInf = getBluetoothInterface()) == NULL) {
ALOGE("Bluetooth module is not loaded");
return;
}
if (sBluetoothA2dpInterface !=NULL) {
ALOGW("Cleaning up A2DP Interface before initializing...");
sBluetoothA2dpInterface->cleanup();
sBluetoothA2dpInterface = NULL;
}
......
if ( (sBluetoothA2dpInterface = (btav_interface_t *)
btInf->get_profile_interface(BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_ID)) == NULL) {
ALOGE("Failed to get Bluetooth A2DP Interface");
return;
}
if ( (status = sBluetoothA2dpInterface->init(&sBluetoothA2dpCallbacks,
maxA2dpConnections, multiCastState,
offload_capabilities)) != BT_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
ALOGE("Failed to initialize Bluetooth A2DP, status: %d", status);
sBluetoothA2dpInterface = NULL;
return;
}
}
classInitNative 的作用上按照方法名找到 java类 中的方法ID , 这样当底层有信息返回时可以通过这些方法直接调用到 java 类的方法。
initNative 的作用是获取 bluedroid 中的 BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_ID 接口并调用其中的 init , init 中会包将刚才classInitNative 获取到的 callback 函数指针传给 bluedroid 。
2.2.3 bluedroid interface
bluedroid 中 A2DP 的 interface 定义如下 , get_profile_interface(BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_ID) 获取到的也是他 :
@ hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/bt_av.h
typedef struct {
/** set to sizeof(btav_interface_t) */
size_t size;
/**
* Register the BtAv callbacks
*/
bt_status_t (*init)( btav_callbacks_t* callbacks , int max_a2dp_connections,
int a2dp_multicast_state, const char *offload_cap);
bt_status_t (*connect)( bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr );
bt_status_t (*disconnect)( bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr );
void (*cleanup)( void );
/** Sends Audio Focus State. */
void (*set_audio_focus_state)( int focus_state );
/** Sets the audio track gain. */
void (*set_audio_track_gain)( float gain );
/** Send priority of device to stack*/
void (*allow_connection)( int is_valid , bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr);
} btav_interface_t;
再来看 bluedroid 中的实现
@ system/bt/btif/src/btif_av.c
static const btav_interface_t bt_av_src_interface = {
sizeof(btav_interface_t),
init_src,
src_connect_sink,
disconnect,
cleanup_src,
NULL,
NULL,
allow_connection,
};
bluedroid 中的更多介绍可以看后续的笔记。