1.架构
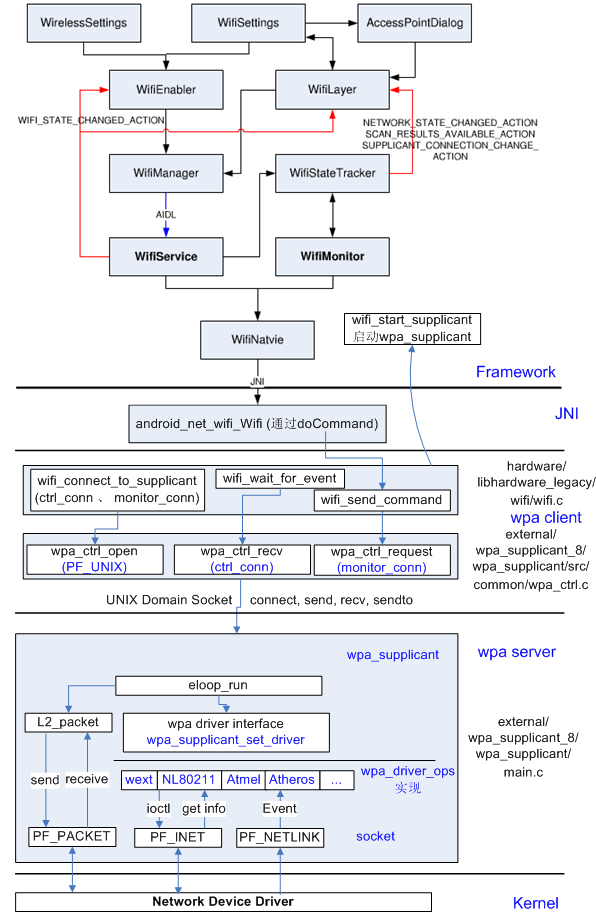
framework 提供的接口为 android.net.wifi ( frameworks/base/wifi/java/android/net/wifi ),app直接通过其中的接口(主要有 WifiManager )来控制 wifi 。 其通过binder来调用wifiservice的服务,实际上 wifiservice 通过 socket 连接来向 wpa_supplicant 发送cmd,来实现对wifi的操作.
2.WifiService
WifiService 是 Android Java Framework 中负责 Wi-Fi 功能的核心服务。在开机时由 SystemServer 启动。
SystemServer.java
private static final String WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS = "com.android.server.wifi.WifiService";
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WIFI_SERVICE_CLASS);
WifiService.java
public final class WifiService extends SystemService {
public WifiService(Context context) {
super(context);
mImpl = new WifiServiceImpl(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
// bind SystemServer
publishBinderService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE, mImpl);
}
WifiService 的主要工作都是在 WifiServiceImpl 中完成:
public WifiServiceImpl(Context context) {
mContext = context;
// 从系统属性“wifi.interface”中取出无线网络设备接口名。 默认值为“wlan0”
mInterfaceName = SystemProperties.get("wifi.interface", "wlan0");
mTrafficPoller = new WifiTrafficPoller(mContext, mInterfaceName);
// 创建一个WifiStateMachine对象, 它是WifiService相关模块中的核心
mWifiStateMachine = new WifiStateMachine(mContext, mInterfaceName, mTrafficPoller);
mWifiStateMachine.enableRssiPolling(true);
// 和BatteryStatsService交互
mBatteryStats = BatteryStatsService.getService();
mPowerManager = context.getSystemService(PowerManager.class);
mAppOps = (AppOpsManager)context.getSystemService(Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE);
mUserManager = UserManager.get(mContext);
// 用于获取和修改 Settings 的 sqlite DB
mSettingsStore = new WifiSettingsStore(mContext);
// 广播事件注册等处理
HandlerThread wifiThread = new HandlerThread("WifiService");
wifiThread.start();
// mClientHandler 用于 AsyncChannel, 其交互对象来自WifiManager
mClientHandler = new ClientHandler(wifiThread.getLooper());
// mWifiStateMachineHandler也用于AsyncChannel,其交互对象来自WifiStateMachine
mWifiStateMachineHandler = new WifiStateMachineHandler(wifiThread.getLooper());
mWifiController = new WifiController(mContext, this, wifiThread.getLooper());
}
其中WifiStateMachine是WifiService中的核心 ,先来看一下它的构造函数 :
public WifiStateMachine(Context context, String wlanInterface,
WifiTrafficPoller trafficPoller) {
super("WifiStateMachine");
mContext = context;
// 获取 countery code
mSetCountryCode = Settings.Global.getString(mContext.getContentResolver(), Settings.Global.WIFI_COUNTRY_CODE);
mInterfaceName = wlanInterface;
// 创建一个NetworkInfo, 它实际上代表一个网络设备的状态信息( status of a network interface)
mNetworkInfo = new NetworkInfo(ConnectivityManager.TYPE_WIFI, 0, NETWORKTYPE, "");
// 创建和NewtorkManagmentService交互的Binder客户端
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.NETWORKMANAGEMENT_SERVICE);
mNwService = INetworkManagementService.Stub.asInterface(b);
// WifiNative: 用于和wpa_supplicant交互
mWifiNative = new WifiNative(mInterfaceName);
// WifiConfigStore: 它对应一个配置文件,该文件用于存储每个无线网络的配置项, 例如代理地址、 静态IP地址等。
mWifiConfigStore = new WifiConfigStore(context,this, mWifiNative);
mWifiAutoJoinController = new WifiAutoJoinController(context, this,mWifiConfigStore, mWifiConnectionStatistics, mWifiNative);
// WifiMonitor: 内部将创建一个线程, 并借助WifiNative去接收并处理来自WPAS的信息。
mWifiMonitor = new WifiMonitor(this, mWifiNative);
// WifiInfo用于存储手机当前连接上的无线网络的一些信息, 包括IP地址、 ssid等内容
mWifiInfo = new WifiInfo();
// SupplicantStateTracker用于跟踪WPAS的状态, 它也是一个StateMachine
mSupplicantStateTracker = new SupplicantStateTracker(context, this, mWifiConfigStore, getHandler());
mNetworkInfo.setIsAvailable(false);
// 状态机初始化
......
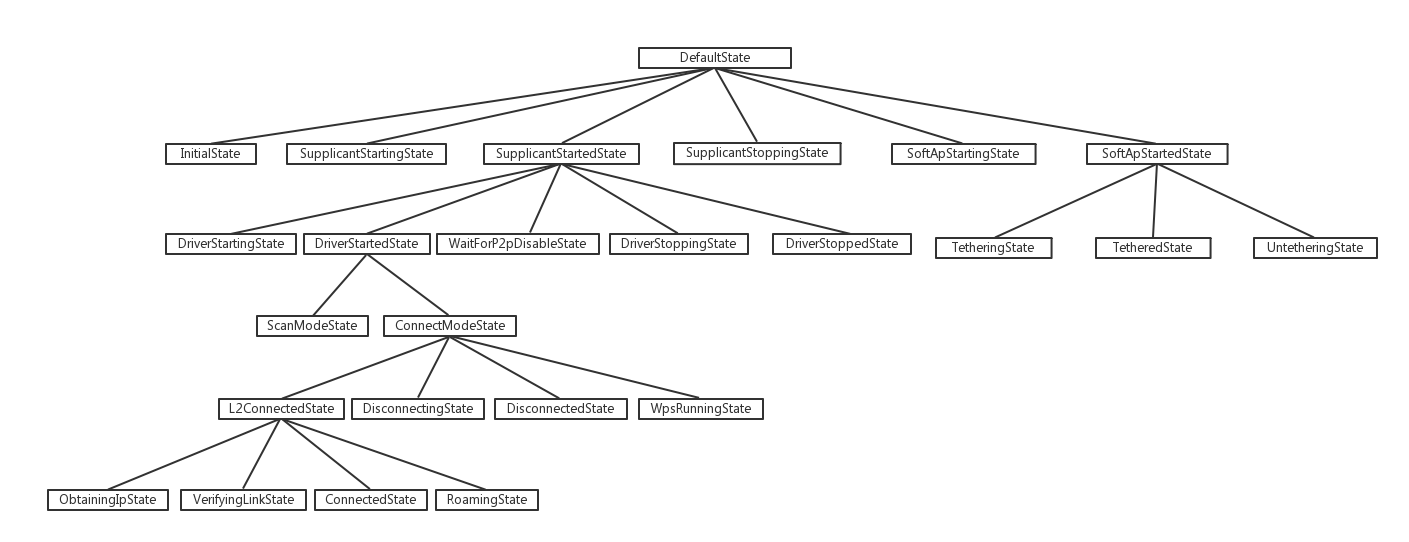
以下为状态机的各个状态 ,其初始状态为 InitialState :
2.1 WifiNative
下面重点看一下 WifiNative , 它用于和 WPAS 通信,其内部定义了较多的native方法( 对应的JNI模块是android_net_wifi_Wifi) 。下面介绍其中最重要的两个方法 :
startSupplicant
用于启动WPAS, startSupplicant是一个native函数, 其 JNI 函数为 android_net_wifi_startSupplicant, 代码如下所示。
android_net_wifi_Wifi.c::android_net_wifi_startSupplicant
static jboolean android_net_wifi_startSupplicant(JNIEnv* env, jobject, jboolean p2pSupported)
{
return (::wifi_start_supplicant(p2pSupported) == 0);
}
wifi.c::wifi_start_supplicant
int wifi_start_supplicant(int p2p_supported)
{
char supp_status[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = {'\0'};
int count = 200; /* wait at most 20 seconds for completion */
const prop_info *pi;
unsigned serial = 0, i;
if (p2p_supported) {
strcpy(supplicant_name, P2P_SUPPLICANT_NAME); //P2P_SUPPLICANT_NAME[] = "p2p_supplicant";
strcpy(supplicant_prop_name, P2P_PROP_NAME);
/* Ensure p2p config file is created */
if (ensure_config_file_exists(P2P_CONFIG_FILE, SUPP_CONFIG_TEMPLATE) < 0) {
ALOGE("Failed to create a p2p config file");
return -1;
}
} else {
strcpy(supplicant_name, SUPPLICANT_NAME); //SUPPLICANT_NAME[] = "wpa_supplicant";
strcpy(supplicant_prop_name, SUPP_PROP_NAME); //SUPP_PROP_NAME[] = "init.svc.wpa_supplicant";
}
// 如果WPAS已经启动, 则直接返回
if (property_get(supplicant_prop_name, supp_status, NULL)
&& strcmp(supp_status, "running") == 0) {
return 0;
}
/* Before starting the daemon, make sure its config file exists */
if (ensure_config_file_exists(SUPP_CONFIG_FILE, SUPP_CONFIG_TEMPLATE) < 0) {
ALOGE("Wi-Fi will not be enabled");
return -1;
}
// entropy文件, 用于增加随机数生成的随机性
if (ensure_entropy_file_exists() < 0) {
ALOGE("Wi-Fi entropy file was not created");
}
// 关闭之前创建的wpa_ctrl对象
wpa_ctrl_cleanup();
/* Reset sockets used for exiting from hung state */
exit_sockets[0] = exit_sockets[1] = -1;
/*
通过设置“ctrl.start”属性来启动wpa_supplicant服务。 该属性将触发
init fork一个子进程用于运行wpa_supplicant。 同时, init还会添加一个新的属性
“init.svc.wpa_supplicant”用于跟踪wpa_supplicant的状态。
*/
pi = __system_property_find(supplicant_prop_name);
if (pi != NULL) {
serial = __system_property_serial(pi);
}
property_get("wifi.interface", primary_iface, WIFI_TEST_INTERFACE);
property_set("ctl.start", supplicant_name);
sched_yield();
while (count-- > 0) {
if (pi == NULL) {
pi = __system_property_find(supplicant_prop_name);
}
if (pi != NULL) {
/*
* property serial updated means that init process is scheduled
* after we sched_yield, further property status checking is based on this */
if (__system_property_serial(pi) != serial) {
__system_property_read(pi, NULL, supp_status);
if (strcmp(supp_status, "running") == 0) {
return 0;
} else if (strcmp(supp_status, "stopped") == 0) {
return -1;
}
}
}
usleep(100000);
}
return -1;
}
connectToSupplicant
另外一个比较重要的函数就是 connectToSupplicant ,它将通过WPAS控制API和WPAS建立交互关系。
int wifi_connect_to_supplicant()
{
static char path[PATH_MAX];
// char IFACE_DIR[] = "/data/system/wpa_supplicant" ,目前看到的手机中都没有这个路径
if (access(IFACE_DIR, F_OK) == 0) {
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s", IFACE_DIR, primary_iface);
} else {
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "@android:wpa_%s", primary_iface);
}
return wifi_connect_on_socket_path(path);
}
int wifi_connect_on_socket_path(const char *path)
{
char supp_status[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = {'\0'};
// 判断wpa_supplicant进程是否已经启动
if (!property_get(supplicant_prop_name, supp_status, NULL)
|| strcmp(supp_status, "running") != 0) {
ALOGE("Supplicant not running, cannot connect");
return -1;
}
// 创建第一个wpa_ctrl对象, 用于发送命令
ctrl_conn = wpa_ctrl_open(path);
// 创建第二个wpa_ctrl对象, 用于接收unsolicited event
monitor_conn = wpa_ctrl_open(path);
// 必须调用wpa_ctrl_attach函数以启用 unsolicited event接收功能
if (wpa_ctrl_attach(monitor_conn) != 0) {
......
}
// 创建一个socketpair, 它用于触发WifiNative关闭和WPAS的连接
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, exit_sockets) == -1) {
......
}
return 0;
}
之后在 wifi.c中, wifi_send_command 会使用ctrl_conn中的wpa_ctrl对象向WPAS发送命令并接收回复, 而 wifi_ctrl_recv 函数将使用monitor_conn中的wpa_ctrl对象接收来自WPAS的消息。
2.2 WifiMonitor
WifiMonitor最重要的内容是其内部的WifiMonitor线程, 该线程专门用于接收来自WPAS的消息。
private static class MonitorThread extends Thread {
......
public MonitorThread(WifiNative wifiNative, WifiMonitorSingleton wifiMonitorSingleton) {
super("WifiMonitor");
mWifiNative = wifiNative;
mWifiMonitorSingleton = wifiMonitorSingleton;
}
public void run() {
if (DBG) {
Log.d(TAG, "MonitorThread start with mConnected=" +
mWifiMonitorSingleton.mConnected);
}
//noinspection InfiniteLoopStatement
for (;;) {
if (!mWifiMonitorSingleton.mConnected) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "MonitorThread exit because mConnected is false");
break;
}
// waitForEvent内部会调用wifi.c中的wifi_wait_on_socket -> wifi_ctrl_recv 函数
String eventStr = mWifiNative.waitForEvent();
......
// 事件处理
if (mWifiMonitorSingleton.dispatchEvent(eventStr)) {
if (DBG) Log.d(TAG, "Disconnecting from the supplicant, no more events");
break;
}
}
}
}
2.3 WifiController
WifiController 也是一个状态机 , 其状态如下图:
![]()
if (isScanningAlwaysAvailable) {
setInitialState(mStaDisabledWithScanState);
} else {
setInitialState(mApStaDisabledState);
}
待补充…